
People want and need your services
Happy New Year!
Welcome to the First Newsletter of the New Year!
Thank you for being a valued subscriber and for your continued support throughout the past year. We truly enjoy creating these newsletters and hope they provide you with valuable insights to help you achieve your goals.
Our focus remains on practice growth and business development. We aim to assist you in enhancing both the quality and quantity of your services—ultimately boosting your bottom line. Along the way, we want to ensure you and your team enjoy the journey.
Don’t forget, Lisa, our expert in insurance, credentialing, and practice sales, also sends out a newsletter on the first Thursday of each month. Feel free to reach out to her anytime for expert advice. (Details about Lisa can be found below.)
CHIROPRACTIC GROWTH: A POSITIVE OUTLOOK
To kick off the New Year, our message is simple: Stay positive and goal-driven!
There is so much to be optimistic about, and I’ll be sharing solid reasons for this in the upcoming weeks. But let’s begin with one key piece of good news—the growth of chiropractic and natural healthcare.
The chiropractic profession is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.3% between 2023 and 2033. This means the industry could grow from a yearly value of $571 million in 2023 to nearly $6 billion by 2033!
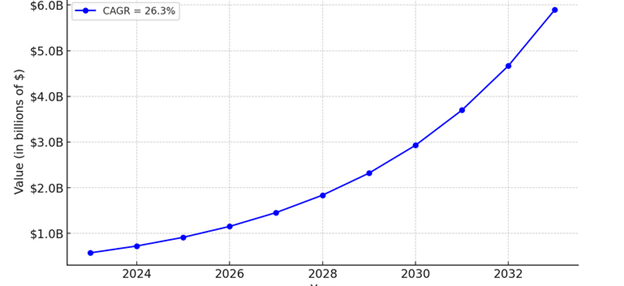
In comparison, the dental market is expected to grow at a much slower rate of just 4% annually.
While some forecasts for chiropractic growth are more conservative, most predict an increase of at least 10%. The study I reference appears to be well-researched, and you can read more about it on our blog (link below).
IT’S NOT JUST CHIROPRACTIC—NATURAL HEALTHCARE IS BOOMING
The growth isn’t limited to chiropractic care. Naturopathy, for example, is expected to grow by 15-20% over the next decade.
The organic food market has experienced significant growth as well. Sales, which were about $13 billion in 2005, surged to $64 billion in 2023 and are projected to reach $144 billion by 2032.
Similarly, the U.S. supplement market has exploded. In 2000, it was valued at $15 billion; in 2023, it reached $53 billion.
WHAT’S DRIVING THE GROWTH IN NATURAL HEALTHCARE?
The reasons behind this surge in natural healthcare are clear—especially for those of you working directly with patients. Americans are increasingly looking for ways to improve their health, and what’s been promoted to them for decades is no longer cutting it. As a result, they are turning to alternative solutions.
When comparing the health of Americans to other industrialized nations, the U.S. ranks near the bottom. Surveys indicate a significant shift in consumer attitudes towards proactive health management rather than reactive, symptom-focused treatments. There is also a growing preference for non-invasive, drug-free approaches.
In many cases, people are turning back to simpler, more natural remedies—sometimes even relying on what “Grandma knew”—as they seek alternatives to pharmaceuticals due to concerns about side effects and dependency.
Other key factors driving the growth of chiropractic and natural health include:
- Increasing Awareness and Acceptance: More people are becoming aware of the numerous benefits of chiropractic care.
- An Aging Population and Active Lifestyles: The incidence of conditions like back pain, arthritis, and sports injuries is on the rise—especially among seniors and those with sedentary lifestyles. Many are looking for non-surgical solutions, and with professional football teams utilizing chiropractors, weekend athletes are following suit.
- Integration with Traditional Medicine: There’s an increasing trend of collaboration between chiropractors and other healthcare providers. In fact, I personally know chiropractors working in hospital settings.
- Affordability: Chiropractic care is generally more cost-effective compared to many conventional medical treatments.
Your future looks bright – keep smiling!
As you can see, the future for chiropractic and natural healthcare is incredibly promising. Keep moving forward with optimism and a focus on your goals.
Let’s work together to make America healthier, one patient at a time!
For auld lang syne, my friend,
Ed
References on blog [LINK]

